Average Usage is by Month
Multiply by 24 (2 * average usage per year is the EOQ formula)
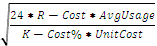
The Replenishment Parameters in this section detail the information that set in Replenishment Parameter Maintenance.
For the following defined scenarios, the system will generate an alert for handling in the Exception Control Center (ECC) according to the hierarchy defined in the Replenishment Parameter Maintenance.
Alert on Non-Replenishment Items with Hits
Alert on Expiring Parameters
Usage Alert Settings
Alert on Product to Arriving Too Early/Too Late for Demand
Alert on Calculated VS. Frozen Order Point / Line Point / Order Quantity Variance
Alert on Unconfirmed Purchase Orders
Alert on Purchase Orders Past Promise Date
Seasonality Analysis Alert
Order Point Adjusters General Settings
Order Point adjusters are parameters that allow the calculated Order Point to reflect replenishment needs based on usage at the customer level. The parameters are applied during the scheduled Replenishment Parameter update. Threshold Minimum, ASQ and Five Hi quantities are all considered when calculating the Order Point based on the Safety Stock and Lead Time for a warehouse/item. The highest of the values obtained from Threshold Minimum, ASQ and Five Hi is used to calculate the Order Point for the warehouse/item. The net result of the order point adjuster is to allow the system to compensate for how a customer’s buying habits are reflected in the purchasing and stocking of an item. This will help prevent stock out situations for normal usage patterns.
The order point helps you determine the right time to buy. A reliable order point is critical; however, it is calculated based on average product usage. As most distributors know, averages don’t always represent customers’ buying habits. The goal of the order point adjusters is to provide a tool for calculating accurate order quantities for those products that experience demand that is infrequent or where order quantities vary considerably from one order to another. This tool will help improve customer service by preventing stock-out situations for products that experience unusual usage patterns. There are three order point adjusters that can be set up: Average shipping Quantity (ASQ), Five-high, and Threshold Minimum.
The following order point adjuster parameters are available:
ASQ / Five HI Months (for usage calculations)
Five-High ASQ (adjuster parameters)
Average Shipment Quantities (ASQ) adjuster parameters
Threshold Minimum Order Point
The Order Quantity is a comparison of the adjusted usage during the review cycle and the EOQ for the item. The greater of the two values is used for the order quantity, and the quantity is rounded to the next standard pack based on the ROQ setting for the item.
The MIN/MAX replenishment model is achieved by setting the Order Point and Line Point values as desired and then setting Frozen Controls to all values with a Freeze Periods of 99.
The EOQ is calculated as
Economic Order Quantity
Average Usage is by Month
Multiply by 24 (2 * average usage per year is the EOQ formula)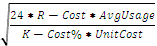
The calculation of appropriate Order Point / Line Point values per Item by Warehouse is instrumental to the AIM process. The factors of Lead Time, Vendor Review Cycle, Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), ASQ, Five-Hi and usage trending are factors in determining an accurate Order Point and Line Point set of values. The addition of daily transactional usage by warehouse and item combination allows these values to be updated to meet the current system state.
The available order quantity parameters are:
OQM for Trend Items ARP Vendor
OQM for non-Trend Items ARP Vendor
OQM for Trend Items ARP Transfer
OQM for non-Trend Items ARP Transfer
Apply Rounding to Order Quantity (See Rounding up Order Quantity)
Rounding Values for ARP Transfer (See Rounding up Order Quantity)
Rounding Values for ARP Vendor (See Rounding up Order Quantity)
The Round up Order Quantity is the UM and quantity that the recommended purchase amount should be rounded up to, usually due to vendor policies.
Item F/M includes an option for “Use ROQ”. This option will round up the recommended order quantity for the item in the Buyers Control Center. The unit of measure to utilize is based on an available buying unit of measure for the item. If a quantity needs to be applied to the specified UM it can be indicated. The default quantity is 1 and must be an integer value for rounding. Additionally, the ROQ can be applied for warehouse transfers or ignored.
When indicated in the Item F/M, the ROQ for an item will be applied to the Recommended Quantity. Items that have been flagged as “Required” will remain in the BCC for processing unless removed by the buyer directly or a full Refresh is performed for the Vendor / Warehouse.
You can implement Round up Order Quantity parameters for the order quantity, ARP Vendors and ARP Transfers:
Apply Rounding to Order Quantity
Rounding Value for ARP Vendor
Rounding Value for ARP Transfer
The Advanced Inventory Management process contains controls that allow automatic replenishment of exceptional products under certain conditions.
FACTS month-end processing functionality employs a number of qualifiers that “freeze” products from being automatically replenished. Examples of frozen products include those with less than six months usage history (new products), products with low demand, and products that experience exceptional or high usage in a particular month. The intention is to force the buyer to review the frozen products and manually adjust ordering controls when necessary. This manual process ensures adequate stock levels are maintained for these “exceptional” products and customer service is not adversely affected. When ‘freezing’ products that qualify under these controls, an exception record is created. The Exception Control Center (ECC), specifically, provides a method for reporting exception notifications to the buyer instead of freezing those products.
You can view products in Flagged Item Report (ICR830) that have been previously frozen. This exception will show frozen products that are due to be unfrozen within the next month. This exception is generated only one time, when IC End of Month Processing is run at month end, and is dependent upon the Frozen Controls fields in Warehouse Item F/M (ICF920).
The available frozen controls parameters are:
Freeze Order Point / Line Point / Order Quantity
Freeze Lead Time
Freeze Safety Stock
Freeze Rank
Lead time is the amount of time required to replenish a product in your warehouse, from the moment a purchase order is generated in the system, to the moment it is on the shelf and ready to sell. The average lead time is stored for each product in Warehouse/Item F/M. It is updated each time new product is received in PO Receipt Entry. Lead time, expressed as a number of days, is used to calculate a product’s order point, an indicator of “when to buy.”
Order Point = [Usage Rate * (Average Lead Time Days / 28)] + Safety Allowance
Lead time days are also used to calculate safety quantity when safety is defined in Warehouse/Item F/M as a percentage.
There are times when lead time on a particular receipt should be ignored and not factored into the average lead time. Generally, this occurs when a product’s lead time varies significantly from the average, and, if factored into the average, could result in an order point that is too high or too low. Other examples of receipts where you might ignore the lead time include:
When a product was shipped using a faster shipping method to expedite delivery on a specific order
When stock is purchased as a “pre-buy” to take advantage of early purchase discounts, but shipment is delayed
When stock is received in the system long after it actually showed up in the warehouse (delay in data entry)
When a purchase order was not created until the date of receipt
The Lead Time options provide parameters that can be set to monitor exceptional lead times and automatically override lead time. You can set to ignore the lead time on product replenishment transactions in several FACTS functions.
Lead time is calculated by adding the last lead time and the most current lead time and dividing by two. If the next-to-last recorded lead time is over six months old, the last lead time is used (no averaging is performed) or by calculating lead time based on a user-defined number of receipts, over a user-defined number of months.
The available lead time parameters are:
Vendor Approved Replenishment Path (ARP)
Transfer Approved Replenishment Path (ARP)
Receipts Used to Calculate Lead Time
Abnormal Lead Time Parameters for ARP Vendors
Abnormal Lead Time Parameters for ARP Transfers
Ranking is a method of classifying products based on their relationship to other products in your inventory. It is used by your buyer to ensure that products that experience a higher volume of sales are ranked higher, and that replenishment controls are in place to make sure there are always adequate stock levels for the higher ranked products. When products are ranked, they are placed into three or more groups for the purpose of stock control and planning. Called ABC ranking, these groups represent products ranked based on their sales “hits.” Hits are the number of times a product appears on a sales order, warehouse transfer, or lost business transaction, regardless of quantity. These are called line hits. By tracking a product’s line hits, you can rank a product by the volume of transactions it appears on.
The products with the most hits are ranked as A items. A items generally represent a smaller group (15-20%) of products that result in around 75-80% of the annual demand. For the purpose of inventory control and replenishment, the greatest attention should be paid to these A-ranked products.
Products with fewer hits are ranked as B, C, D, and so on (up to 26), based on how your ranking levels are defined. Least attention is paid to the lowest ranks.
The available rank parameters are:
Threshold Minimum Rank for New Items
Rank Parameters
The review cycle and buyer can be designated for transfers. The buyer can be designated for each Approved Replenishment Path (ARP) based on the following matrix.
|
Source |
Purchasing Line |
|
Vendor |
<not specified> |
|
Vendor |
Purchasing Line |
|
From Warehouse |
<not specified> |
|
From Warehouse |
Purchasing Line |
An example is buyer 100 for warehouse 01 can be established for items to be transferred from warehouse 02 for purchasing line “Warehouse Items”. Buyer 200 for warehouse 01 can be established for items to be procured from vendor V100 with no purchasing line set.
For Review Cycle an additional From Warehouse parameter is available in Replenishment Parameter Maintenance. Therefore, it doesn’t fit in the “normal” hierarchy, but rather has its own unique settings for Review Cycle. The hierarchy that the system uses for Review Cycle is as follows:
Warehouse + From Warehouse
Warehouse + Vendor
Warehouse + Purchasing Line
Purchasing line is the most unique, and Vendor and From Warehouse are at the same “level”. The From Warehouse is used for Transfers and Vendor is used for Purchase Orders. Purchasing Line is only used for Purchase Orders as well.
When determining the usage for an item in the Order Point and Line Point calculations, the number of periods for analysis is indicated by the item’s rank. The higher an item’s rank, the fewer the number of periods should be specified. The usage periods by Rank are used in the Backward, Forward and Trending usage analysis for an item.
The available usage parameters are:
Threshold Minimum Usage
Trending Parameters and Adjusters
Usage Months for Seasonal
Usage Months for non-Seasonal
Safety stock, also referred to as safety allowance, is the additional stock you carry in inventory to protect against a stock out. If forms a pad to take care of reasonable variations in usage or lead time from the averages anticipated. Safety allowance is an amount that you define for each product in IC Warehouse/Item F/M (ICF920). It can be entered as days, a percentage, or a quantity. FACTS will convert a days or percentage value to a quantity and use that value to determine the product’s order point.
The available safety stock parameters are:
Safety Stock for Approved Replenishment Path (ARP) Vendor parameters
Safety Stock for ARP Vendor adjusters
Safety Stock for ARP Warehouse Parameters
Safety Stock for ARP Warehouse Adjusters